Output menu¶
Output column submenu¶
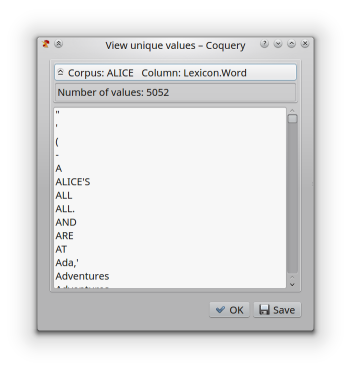
View unique values¶
This function creates an alphabetical list of all occurring values in the column. Each value occurs exactly once in the list. For the column Word in the example above, this corresponds to a list of all word types occuring in the corpus ALICE.
Clicking on the list header expands the header to show the number of unique values in the list. Clicking on the header again hides this number.
Clicking ‘Ok’ closes the Unique value viewer. Clicking ‘Save’ creates a comma-separated text file (CSV) containing all unique values.
Link to external table¶
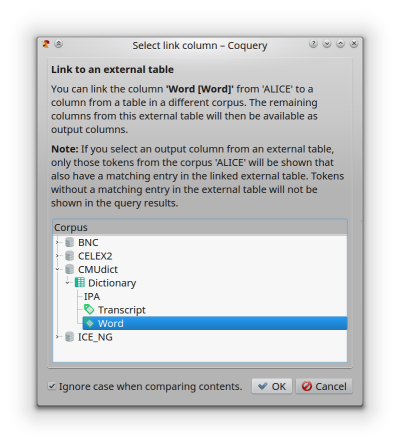
The Link to an external table dialog for the column Word in the table Lexicon from the corpus ALICE.
This function allows to link the current column to another column from a table that is provided by an external corpus. This external table will be shown in the Output columns tree as a subtable of the current column.
If you include an output column from an external table in the results table, Coquery will look up the content of the linked column from the current corpus in the column from the external table selected in this dialog, and display the matching contents from the external table.
Note
If you select an output column from an external table, only those tokens from the current corpus will be shown that also have a matching entry in the linked external table. Tokens without a matching entry in the external table will not be shown in the query results.
By linking columns from the current corpus to external tables in this way, a corpus may be extended with annotations not provided by the corpus itself. For example, a corpus may be extended with part-of-speech labels by linking the Word column to a table from a corpus that contains POS labels. Likewise, phonetic transcriptions may be obtained from e.g. an external pronunciation dictionary.
A column can be linked to more than one external table. To remove a linked external table, right-click on any output column from that external table, and select ‘Remove link’.
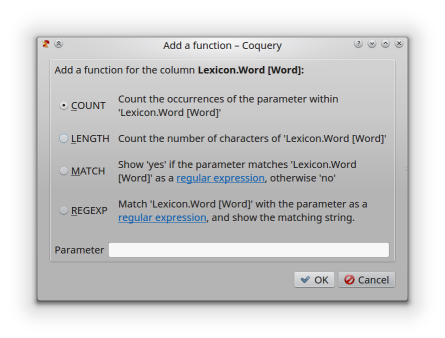
Add a function¶
By using this dialog, a new output column is created, the values of which are calculated on the basis of the values of the current column. The following functions are available:
- COUNT
- LENGTH
- MATCH
- REGEXP
There is an entry field for functions that require an additional parameter.
COUNT counts the number of occurrences of the parameter value in the
current column. For example COUNT with a parameter value of a counts
the number of occurrences of the letter a for each value of the current
column.
LENGTH counts the number of characters for each value of the current column. This function does not use the content of the parameter entry field.
MATCH returns the text yes for each value of the current column that
matches the parameter, or no otherwise. Note that the parameter is
evaluated as a regular expression. For example, MATCH with a parameter
value of ^a|b returns yes for all values in the current column that
begin with either the letter a or the letter b, and no for all other
values.
REGEXP matches each value of the current column with the parameter, and
returns the matching string. For example, REGEXP with a parameter value
of plain.* returns from all values in the current column the substring
that starts with the letter sequence plain, followed by any number of
additional letters. If the parameter does not match a value in the current
column, the function returns an empty string.
The following table illustrates the result of REGEXP(plain.*) for the
Word column from the corpus ALICE:
| Column value | Function result |
|---|---|
| plainly | plainly |
| complaining | plaining |
| explained | plained |
| complained | plained |
| explain | plain |
| learning | |
| considering | |
| promise | |
| clean | |
| ... | ... |
The function output column created in this way can be selected and unselected just like a column that is provided by the corpus itself. To remove a function, right-click on the function output column and select ‘Remove function’.